RPL Debugger
RPL sets can be very large and complicated, and consequently it can be difficult to determine why a set is doing what it is doing. The RPL debugger is designed to help understand the behavior of RPL sets; with this tool the user can pause RPL execution, look at the values of RPL expressions as they are evaluated, and step through RPL execution. The following sections describe the RPL debugger including an overview, how to enable debugging, a tour of the debugger window, and suggested ways of using the debugger.
About RPL Debugging
The RPL Debugger utility provides the following functionality:
• Control execution at a fine granularity. Examples:
– Pause (interrupt) execution.
– Set a breakpoint that pauses execution.
– Continue execution.
– Step, i.e., execute the next line of code, optionally descending into called functions.
• Visualize the currently executing RPL logic and data when the program is interrupted, either because an error was encountered or because the user paused execution through the debugger. The RPL policy editors provide a debug cursor which provide visual indication of the current line (i.e., the next line to be executed) and a mechanism for displaying a textual representation of the current values of expressions.
• Visualize and traverse the call stack when the program is interrupted. This consists of a list of the names of the blocks and functions currently in the call stack with an indication of the current location in that stack.
• Manage collections of breakpoints, i.e., provide operations such as add, delete, temporarily disable.
RPL is used in several contexts within RiverWare; currently they are:
• Rulebased simulation (RBS)—Ruleset
• Object level user defined accounting methods—Method set
• Initialization Rule—Ruleset
• Iterative MRM—Ruleset
• Optimization Policy—Goal set
• Expression slots
Except for this last application (Expression slots), RPL policy is organized at the RPL group level into functions and blocks of RPL statements, variously called rules, goals, or methods. Statements can be nested and contain expressions, which might contain function calls. Expression slots and functions are defined by a single RPL expression.
RPL execution can be paused before/after each of these locations and before/after each RPL expression.
When execution is paused, use the debugger to view the values to which expressions have evaluated up to that point. Each time a block of statements or an expression slot is executed, results from any previous evaluations are cleared, so one must pause after the expression or statement to see the values to which its expressions last evaluated.
Enabling RPL Debugging
To enable this feature, use one of the following approaches:
• From the RPL Debugger (Policy, then RPL Debugger), use the button on the menu bar.
• From the RPL Debugger (Policy, then RPL Debugger), use the Debug, then Enable RPL Debugging menu.
Debugging enable/disabled status is a workspace setting applies to the execution of all RPL policy associated with the current model. This setting is saved with the model.
When debugging is first enabled, buttons are added to the Run Control window to indicate the state of the RPL Debugger.
Select the RPL Debugger Enabled/Disabled button to enable or disable. This button remains in place for that RiverWare session. To hide or show the button, use the View, then Show RPL Debugging button. Once shown, you can use this button to enable/disable the debugger. To open the RPL Debugger, select the bug button:

Caution: Enabling debugging can have a significant negative impact on performance!
There are two distinct performance impacts of debugging:
• Retaining values on expressions. Normally, RPL execution is optimized for efficiency, and thus during execution values are reused where possible and intermediate results are not retained. To retain values for debugging requires additional memory and time to copy intermediate results.
• Computational overhead. To support the interruption of RPL execution at each point at which a pause might occur, RiverWare must check if a pause is in fact appropriate for that location.
Since both of these impacts can be significant, by default RiverWare does not enable these processes. Rather the user only incurs the additional overhead of debugging when they have indicated that they would like interactive debugging as described above.
See RPL Debugger Scenario 1 for a scenario in which the user might want to disable and then enable debugging temporarily.
Tip: You can’t disable debugging while paused in the debugger. Clicking the button has no impact. You must get out of the debugger to disable it.
The RPL Debugger
The RPL Debugger is accessible as follows:
• From the Workspace Policy menu (Policy, then RPL Debugger)
• From any RPL Block (Set, Rule, Goal, Method, Function, etc.), then Debugger menu
• Using the F8 shortcut when any RPL window is selected
• From the Run Control using the RPL Debugger button:

This window displays information about RPL execution and allows the user to control RPL execution. Figure 4.6 shows the principle components of this window.
Figure 4.6 Tour of the RPL Debugger
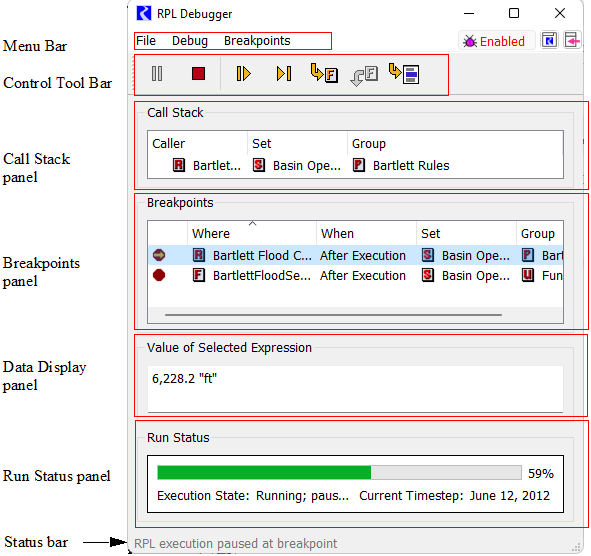
• Menu bar. Menu access to debugger functionality, including a button to enable and disable..
• Control tool bar. Buttons for controlling RPL execution.
• Call Stack panel. Describes the location at which RPL execution is paused (when it is paused).
• Breakpoints panel. Lists the locations at which the user has requested that execution regularly pause.
• Data Display panel. Displays the value to which the selected expression last evaluated.
• Error message panel. When an error occurs during RPL execution, a description of that error; see Error Handling for details.
• Run Status panel. Shows the overall run status including the current controller timestep.
• Status bar. Brief description of the state of the debugger.
Menu Bar
Table 4.1 describes the functionality available through the File and Breakpoints menus. See Control Tool Bar and Debug Menu for details about Debug menu.
Menu | Sub-menu | Keyboard accelerator | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
File | Close | Ctrl+w | Close the RPL Debugger |
Breakpoints | Enable Breakpoint | F9 | Enable (or disable) the selected breakpoint |
Breakpoints | Delete Breakpoint | Shift+F9 | Delete the selected breakpoint |
Breakpoints | Delete All Breakpoints | Ctrl+Shift+F9 | Delete All Breakpoints |
Control Tool Bar and Debug Menu
In addition to the existing mechanisms for controlling a run (e.g., the pause button of the run control), through the debugger the user can control RPL execution. Table 4.2 describes the button controls in the control toolbar and Debug menu of the Debugger window.
Menu Item | Button | Keyboard accelerator | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Enable RPL Debugging |  | Turn on or off the collection of RPL debugging information. See Enabling RPL Debugging for debugging information. | |
Pause |  | Ctrl+c | During RPL evaluation, pause at the next opportunity. When RPL execution is paused, the user can visualize the state of the system in the following ways: • Examine the value to which any RPL expression last evaluated. • Examine the current call stack. • Examine the workspace or otherwise interact with any of the RiverWare windows. Some of this functionality is available as well after a run has terminated. The user is strongly discouraged from making any changes to the model or policy (and is prevented from exiting RiverWare) while RPL execution is paused. |
Stop |  | Shift+F5 | Abort RPL execution. If in a run, stop the run at the next available opportunity. The user is not presented with the usual abort run notification message but a green diagnostic is posted. |
Continue |  | F5 | When execution is paused, continue execution until one of the following occurs: • A breakpoint is reached. • The user requests another pause or stop event. • RPL execution terminates normally. |
Step |  | F10 | When execution is paused, continue execution and pause at the next legal spot for pausing execution which is at an equal or lesser depth in the call stack, including each expression or statement. Tip: Because the debugger can pause before or after each expression, stepping can be a tedious way to advance through RPL logic. Instead, select the expression you want to go to and use the Continue to Selection operation described below. |
Step Into |  | F11 | When execution is paused, continue execution and pause at the next legal spot for pausing execution including each expression or statement called as well as stepping into functions called.See the tip above. |
Step Out |  | Shift+F11 | When execution is paused within a function, continue execution and pause at the next legal spot for pausing execution which is at a lesser depth in the call stack (i.e., continue to the next pausable location in the calling function). |
Cont. to Sel. |  | F12 | When execution is paused, continue execution until the selected RPL expression is about to be executed (or execution is interrupted for some other reason, e.g., another breakpoint). This action is functionally equivalent to: set breakpoint before selection, continue, remove breakpoint |
Show Button Labels | Show the labels on the toolbar buttons. (shown above) |
The control toolbar can be repositioned within the window. By default, the buttons are unlabeled, but text labels can be displayed by selecting Debug, then Show Button Labels. All of the control actions are also available via the Debug menu or by keyboard shortcuts. For the most part, the shortcuts are the same as those used by Microsoft Visual Studio for the comparable action.
Call Stack Panel
When RPL execution is paused in the debugger, the Call Stack panel describes the current execution location. The display is a tree-view list of the items which have are currently executing. Double-clicking an item in a row in this list opens the associated editor. For each item in the call chain, its Caller, Group, and Set are listed. For functions, the argument types, names, and values are displayed as optionally displayed children of that row. Figure 4.7 illustrates.
Figure 4.7 RPL Debugger Call Stack panel
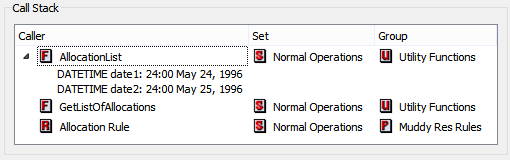
Breakpoints Panel
The Breakpoints panel lists locations at which the user has requested that execution regularly pause. Double-clicking a row opens the editor for that item. For each breakpoint, the panel displays the following:
• Icon. Red octagonal breakpoint indicator, filled indicates that it is enabled  , unfilled indicates disabled
, unfilled indicates disabled  . Selecting the stop sign indicator will enable/disable the breakpoint.
. Selecting the stop sign indicator will enable/disable the breakpoint.
 , unfilled indicates disabled
, unfilled indicates disabled  . Selecting the stop sign indicator will enable/disable the breakpoint.
. Selecting the stop sign indicator will enable/disable the breakpoint.• Where. Name of the item containing the breakpoint. The breakpoint name includes an identifier which indicates the statement with which the breakpoint is associated. It is a hierarchical ID which looks like: <block/rule priority>.<statement index>.<statement index>. For breakpoints on expressions, only the statement and index are listed. Double click to open the RPL window and the expression will be selected.
• When. If it will break before or after execution of that item.
• Set. Set (where applicable) that contains that item.
• Group. Group (where applicable) that contains that item.
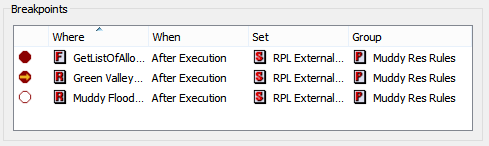
The list may be sorted based on any column; initially it is sorted based on the name of the item containing the breakpoint. Also the columns may be rearranged by dragging the column label.
When RPL execution pauses at a breakpoint, the associated row in the Breakpoints Panel is scrolled into view. While execution is paused at a breakpoint, the breakpoint indicator contains a yellow arrow (the debug cursor)  .
.
 .
.Breakpoints can be created and deleted within the RPL editor for the corresponding item; see Sample Use Scenarios for details. Within the RPL Debugger, they can be deleted and/or temporarily disabled/enabled using the Breakpoints menu. Also, selecting the stop sign indicator will enable/disable the breakpoint. Breakpoints are persistent (saved with the RPL item which contains the breakpoint).
Value of Selected Expression Panel
When paused, the Value of Selected Expression panel displays the value of the selected RPL expression. See Displaying Data Values for details.
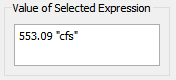
Run Status Panel
The Run Status panel at the bottom of the debugger shows the overall status of the run. This information is also shown on the Run Control / Run Status. The panel in the debugger provides easy access to the current controller timestep.
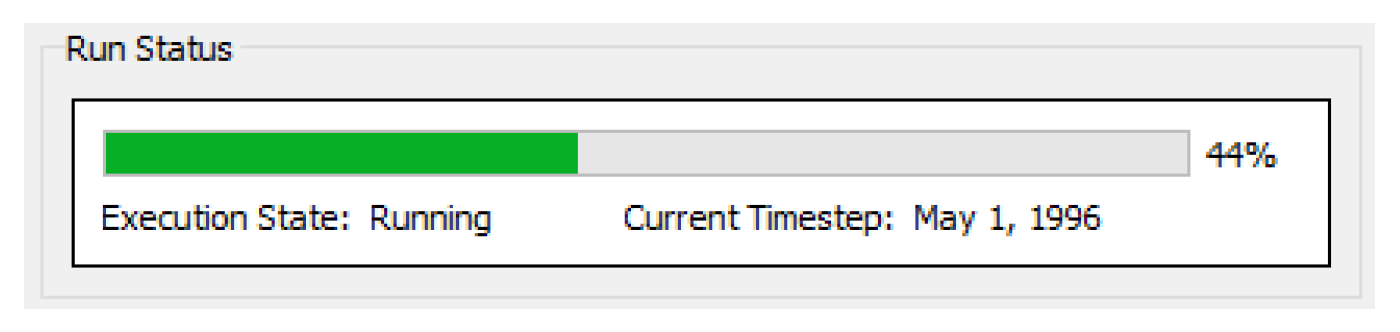
Using the RPL Debugger
Following is a description of how to use the RPL Debugger. In general, the approach is: add breakpoints, start execution, execute to the breakpoint and pause, investigate values at that breakpoint, continue or step to the next location of interest, and continue looking at values and stepping/continue until satisfied. The process becomes more complicated when you wish to investigate the values at one timestep or location within a long run. See Sample Use Scenarios for a description of this scenario.
Adding Breakpoints to RPL Windows
RPL breakpoints can be added at the following locations:
• Before any expression
• After any expression
• Before any statement in a rule, optimization goal, or user-defined accounting method
• After all statements in a rule, optimization goal, or user-defined accounting method
• Before the execution constraint in a rule, optimization goal, or user-defined accounting method
• After the execution constraint in a rule, optimization goal, or user-defined accounting method
• Before a function’s body expression
• After a function’s body expression
• Before an expression slot’s expression
• After an expression slot’s expression
Setting a breakpoint at a particular location will cause execution to pause each time that location is reached. If there is a breakpoint associated with a given location, a solid red octagon is drawn in the debugging margin (unfilled red octagon for disabled breakpoints).
Note: The debugging indicators are sized to match the font, which may be changed in the RPL Display settings in the Settings Manager. See Font in RiverWare Policy Language (RPL).
When debugging is enabled, RPL editors display a left margin. When you select the margin, the behavior is as follows:
• If there is no breakpoint, select to add a breakpoint. Selecting to the left of the RPL item will add the breakpoint before. Selecting just to the left and below will add it after the breakpoint.
• If there is an enabled breakpoint, select the breakpoint to disable it.
• If there is a disabled breakpoint, select the breakpoint to delete it.
Thus, selecting the margin cycles through three states, enabled, disabled, and deleted.
Breakpoints may be added/removed from the selected expression using the Rule/Methods/Goal(block), then Break Before/After Selected Statement or Execution Constraint menu actions.
Breakpoint Locations
There are two main locations in which breakpoints can be created:
• Statements, functions, and execution constraints, and
• Expressions.
In general, breakpoints on individual expressions are only needed for debugging loop operators like the FOR, WHILE, SUM, and AVE. The two approaches are described as follows:
Breakpoints on Statements, Functions, and Execution Constraints
For statements, functions and execution constraints, the breakpoint indicator is associated with the block of code and appears in the RPL frame margin. Figure 4.8 illustrates both the margin and the enabled and disabled status.
Figure 4.8 Breakpoints on Statements, Functions and Execution Constraints
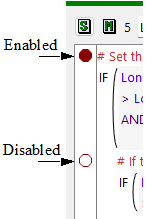
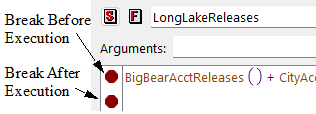
Figure 4.9 illustrates two breakpoints on a function body. The breakpoint after execution is below the last expression.
Figure 4.9 Breakpoints on Function Bodies
Breakpoints on RPL Expressions
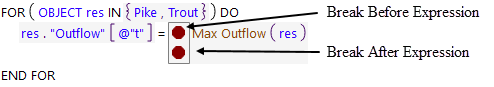
For expressions, the breakpoint indicator appears in the editor and appears just to the left of the expression in a margin on the expression. Figure 4.10 illustrates.
Figure 4.10 Breakpoints on Expressions
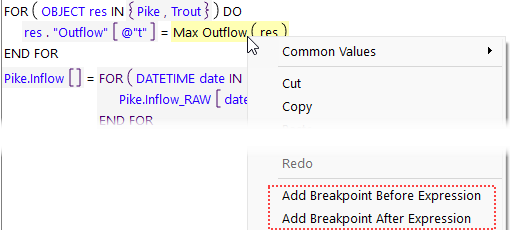
To not clutter up the interface, the margin is only shown if there is a breakpoint or the debugger is paused on that expression. Use the right-click context menu to add the breakpoint as shown in the following figure:
Figure 4.11 Context menu to Add Breakpoint Before/After Expressions
Tip: Use breakpoints on expressions sparingly. As shown in the following screenshot, there are many places to put these breakpoints.
Figure 4.12 RPL Expression with many breakpoints
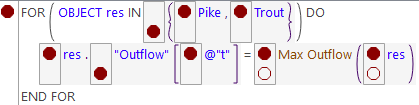
Starting the Debugger
To start the debugger, initiate execution in the standard way depending on the set to be debugged. That is:
• Rulebased simulation ruleset: Start a rulebased simulation run.
• Optimization policy set: Start an optimization run.
• Object level user defined accounting method set: Start an accounting run.
• Initialization Rules: Start a simulation or rulebased simulation run.
• Iterative MRM Ruleset: Start an iterative MRM run.
• Expression slots: Start a run or evaluate the expression slot(s) manually.
The RPL execution will begin and the RPL debugger will pause when it hits a breakpoint or is paused.
When RPL execution is paused, a yellow arrow called the debug cursor  , is shown in the RPL window margin to the left of the statement or expression at which execution is paused. Typically this indicates that the indicated statement/expression is just about to be evaluated.
, is shown in the RPL window margin to the left of the statement or expression at which execution is paused. Typically this indicates that the indicated statement/expression is just about to be evaluated.
 , is shown in the RPL window margin to the left of the statement or expression at which execution is paused. Typically this indicates that the indicated statement/expression is just about to be evaluated.
, is shown in the RPL window margin to the left of the statement or expression at which execution is paused. Typically this indicates that the indicated statement/expression is just about to be evaluated. Note: When paused after execution of a function or the last statement of a block, the debug cursor will not be pointing to a specific function/statement but will appear at the bottom of the window, as shown in Figure 4.13.
Figure 4.13 Debug Cursor Examples

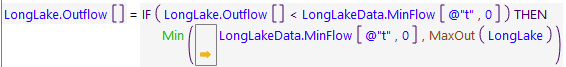
When the debugger is paused on an expression, the cursor is shown in the margin to the left of the expression as shown in the two images.
Figure 4.14 Debugger Cursor Shown Paused on an Expression with a Breakpoint
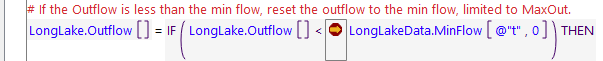
Figure 4.15 Debugger Cursor Shown Paused on an Expression with No Breakpoint
Displaying Data Values
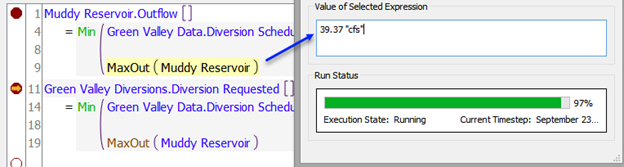
When RPL execution is paused in the debugger, you can interact with most RiverWare windows to examine the current state of the system. The values of interest during a run are the values to which expressions (including sub-expressions, i.e., expressions within expressions) have evaluated, as well as the values set by assignment statements. Select the expression in the RPL editor. Once selected, there are two ways to look at the value of the selected RPL expression:
• Using the Value of Selected Expression panel in the debugger
Figure 4.16 RPL windows showing selected value and Value of Selected Expression panel in the RPL Debugger
• Using tool tips on RPL windows. Tool tips are shown by hovering over the selected expression.
Figure 4.17 RPL window showing selected value and tool tip with the value
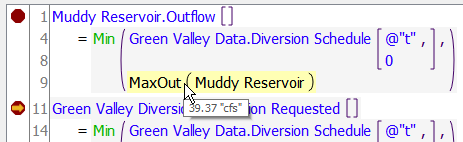
Within the RPL Debugger, Value of Selected Expression panel, most values are displayed as a single value, as shown above. Lists are different as they can contain multiple items and can be very long. Instead, lists are shown in a tree view:
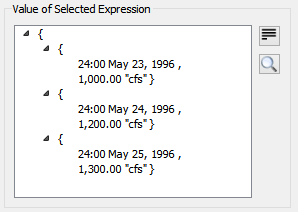
This display shows the levels of the list. Collapsing the list at any level shows the containing list on a single line. For example, this list shows the three sub lists collapsed.
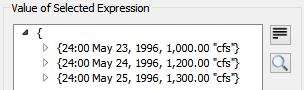
Click the  icon to show the list as a flat view. For example:
icon to show the list as a flat view. For example:
Note: Copy of the list is available from the flat view only. Use the right-click context menu to copy.
The  icon returns it to a tree view.
icon returns it to a tree view.
The  icon pops out the display into a resizable window showing the tree view. This is particularly handy for large lists as you can make the window much larger.
icon pops out the display into a resizable window showing the tree view. This is particularly handy for large lists as you can make the window much larger.
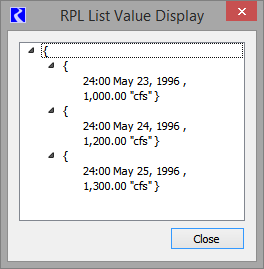
Data Value Units
The value displayed uses the settings in the Unit Schemes; see Unit Schemes in User Interface for details. Whenever a RPL value is displayed in the debugger or in tooltips, RiverWare uses the units defined in the scheme. But, for monthly and annual values, it is sometimes not known within the debugger for which timestep the value is associated. In that case, monthly values assume there are 31days in the month. Annual values assume 365 days in the year.
Stepping, Continuing, and Pausing
Once paused, the you can investigate the values of expressions and then continue on to other breakpoints, step, step into, step out, or continue to selection. These actions are available on the RPL debugger toolbar, menu choices, and keyboard accelerators; see Control Tool Bar and Debug Menu for details.
Also remember that within a run, there are two types of stepping and pausing:
• From the RPL debugger and
• From the Run Control.
For example, within a rulebased simulation run, you select Step on the Run Control to advance the timestep, use the RPL debugger to break in a rule, step through that rule in the RPL debugger and then select Continue on the RPL debugger. The timestep then finishes and the Run Control will pause before the next timestep.
Limitations
There are a few limitations that are imposed by the debugger:
1. Because you are in the middle of executing a RPL item, it would be problematic to delete an object or close RiverWare. Thus, when paused in the debugger, RiverWare prohibits many user actions, such as:
– Exiting RiverWare
– Closing a RPL set
– Clearing the workspace
– Loading a model
2. The debugger will not display the value of the entire left hand side of an assignment statement. Technically, the left hand side is not evaluated, it receives the value to which the right hand side evaluates, so it does not have a value to display. If you wish to see the value that will be assigned, highlight the entire right hand side. Note sub-expressions on the left hand side of an assignment are evaluated, and are available for display (after the statement has been executed).
3. As discussed earlier, enabling debugging incurs performance costs in both memory and CPU usage. The impact is highly model and machine dependent, but most user can expect to see less than a 25% slowdown in RPL execution time.
Error Handling
If an error occurs during RPL evaluation with debugging enabled, the user is presented with an informational window and execution is paused in the debugger. The RPL editor containing the location of the error is raised and the debugging cursor indicates the location of the error. This could be one of the following:
• A statement in a block
• The body of a function
• The expression of an expression slot.
RPL execution is paused as soon as the error occurs, and an informational window is presented to the user. This happens even before an error has been posted to diagnostics, however all of the relevant information concerning the error is displayed within the debugging window:
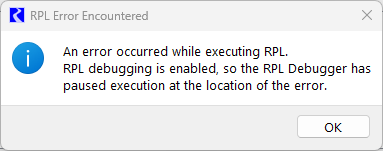
• The call stack contains the items being evaluated at the time of the error
• A panel is displayed that provides an explanation of the error and a textual version of the RPL expression at which the error occurred. This panel is hidden unless there has been an error.
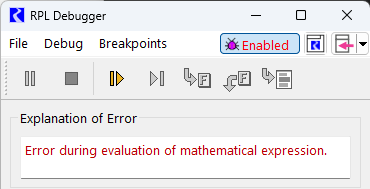
The only action possible through the debugger when the run has been aborted is to continue execution, which will post the error diagnostic and abort the run as usual. 

Sample Use Scenarios
In this section we present a few example scenarios that illustrate different ways to make use of the RPL debugger.
RPL Debugger Scenario 1
The Run Control allows user to specify a timestep/goal at which to pause the run. This is useful for longer model runs when you wish to look at execution on a specific timestep. The following is a possible debugging scenario:
1. Disable RPL debugging; see Enabling RPL Debugging.
2. Configure the Run Control to pause before the desired date, as shown in Figure 4.18.
Figure 4.18 Run Control with Pause Before Timestep Enabled
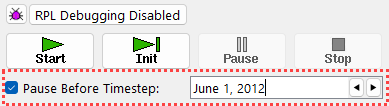
3. Start a run and let it run until it pauses at the timestep indicated.
4. Enable RPL debugging.
5. Set up breakpoints as needed. This could be done at any point. In the initial part of the run, RPL debugging is disabled, so the breakpoints have no effect.
6. Step in the Run Control, to have the controller go into the timestep.
The run proceeds until a breakpoint is reached.
7. Examine RPL values as desired and use the debugger’s Step and Continue buttons to control RPL execution.
8. When finished, delete or disable breakpoints and continue in the RPL debugger and in the Run Control to finish. Or, select the Stop button in the debugger to stop RPL execution and end the run.
RPL Debugger Scenario 2
Because the debugger catches RPL errors and displays the exact location of the error, it can be used in the RPL development process to catch run time errors. For example, when running a model where you just made a lot of RPL changes and you wish to catch runtime errors, use the following steps.
1. Enable debugging but do not set any breakpoints.
2. Run the model or execute the policy.
The model runs, and if a RPL error occurs the RPL debugger will pause execution.
The debugger will display an explanation of the error and open the window indicating the location of the error; see Error Handling for details.
3. Determine what the error is by using debugging tools.
4. Select Continue in the debugger and the run will stop.
5. Fix the error in the RPL window.
Note: The error message is repeated in the diagnostics output.
Revised: 12/01/2025