Two-dimensional Table Interpolation
For two-dimensional interpolation, RiverWare assumes that the values in the x column of the data table are increasing. Table B.1 is an example of the proper way to formulate a table for two-dimensional interpolation.
Pool Elevation (ft) | Storage (acre-ft) |
|---|---|
440 | 439,400 |
441 | 455,900 |
442 | 472,600 |
443 | 489,600 |
445 | 507,000 |
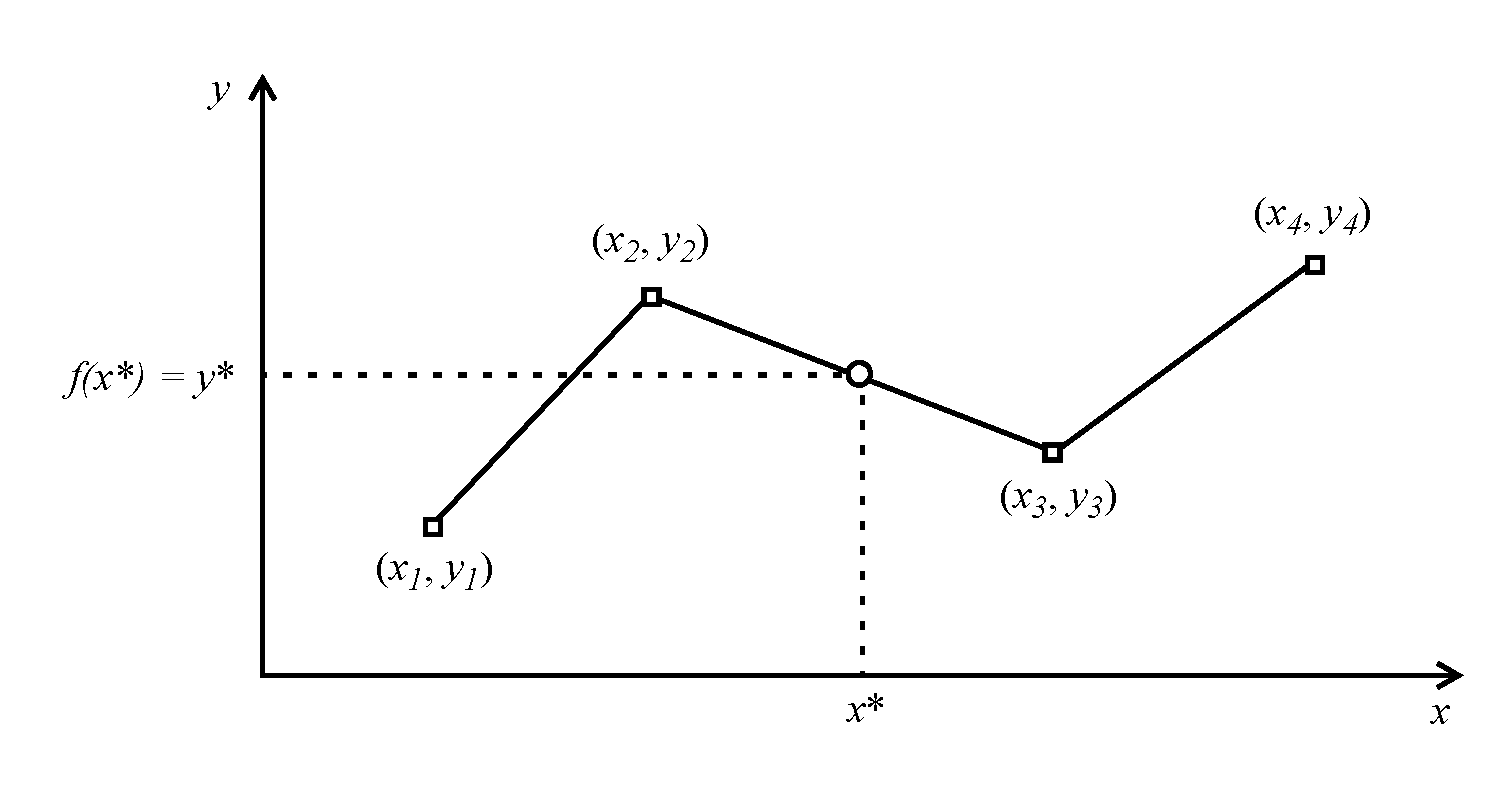
For two-dimensional functions, we apply linear interpolation between data points. Figure B.1 illustrates this approach. We denote a particular approximation using the table by an asterisk: y* = f(x*).
Figure B.1 Two-dimensional linear interpolation
Two-dimensional Table Interpolation Errors
The following types of errors may be reported during two-dimensional table interpolation:
• Invalid value (data error): an x or y value is invalid (xi = NaN or yi = NaN, for some i).
• Non-increasing x (data error): the x values are not increasing (xi >= xi-1, for some i).
• Out of range (interpolation error): the x value being interpolated is out of the range of the table, that is, the domain of the function being approximated (x* < xmin or x* > xmax).
Revised: 07/03/2024