Release Notes Version 3.0
This document describes new features, enhancements, and changes included in RiverWare Version 3.0, released on February 18, 2000. These changes are new to the executable since the release of RiverWare Version 2.1 on March 10, 1999.
Please direct questions to RiverWare Technical Support at (303) 492-0908 or support@cadswes.colorado.edu.
Special Attention Notes:
• The Accounting calculations in RiverWare are still under development. Accounting should only be used by sponsors directly involved with the development process.
• The Optimization solver is available to non-sponsors for the first time in this release. It is a beta version. Please report any problems to CADSWES. Online documents for optimization will be released soon.
• Rulesets saved in the new release CANNOT be used in older executables. There is no message to warn the user about this. Rulesets saved under previous executables CAN be used with the new release however.
• It is important that users do not use the Confluence as a bifurcation object. Specifically, the Inflow slot on a Confluence object should not be linked to the Inflow slot on any other object. A bifurcation object will be available in RiverWare soon.
• For Reach objects solving downstream with the noRouting method, Seepage is now removed before Reach Bank Storage and Gain/Loss calculations when dispatching. Previously Seepage had been removed after Total Gain/Loss was calculated so different values for Total Gain/Loss will now be computed. When solving upstream, Return Flow is now removed before computing Total Gain/Loss resulting in different values for Total Gain/Loss.
• On the Water User object, the name of the Agricultural Requests method in the Diversion and Depletion Request calculation category has been changed to Irrigation Requests. The Agricultural Requests method used in old models is automatically replaced by the Irrigation Requests method.
• On the Reach object, the method category Uncertainty Calculation was changed to Reach Uncertainty Calculation.
• Confluences are now allowed to dispatch before the start of the run. This can result in an overdetermination error before the start of the run if a confluence solves and receives information across a link from another object or if its information propagates to another object.
• The spilledEnergyCalc category is no longer available. Therefore, the Spilled Energy, Spilled Power, and Spilled Energy Power Coefficient slots no longer exist.
• The following slots are converted from type SeriesSlot to AggSeriesSlot: On Reservoir Objects: Tailwater Elevation, Evaporation, Precipitation Volume, Surface Area, Available For Diversion, Change in Bank Storage On Water User and AggDiversionSites: Total Diversion, Total Depletion, Total Return Flow, Total Unused Water, Incoming Available Water, Outgoing Available Water, Diversion, Inflow, and Outflow. These changes will not adversely affect models saved in an older version of RiverWare.
Required Model File Updates
Sequential Linking on AggDiversionSite
Users moving from RiverWare 2.1 or earlier must make the following changes for models using the sequential linking structure on the Aggregate Diversion Site object (changes have already been incorporated in RiverWare 2.1.1, 2.1.2 and 2.1.3. Users of these versions may disregard this notice):
1. The Total Unused Water slot must be linked to the Return Flow slot on the object from which water is being diverted.
2. The link between Total Available Water and the Incoming Available Water slot on the first Water User element must be removed.
If a large number of objects require these changes, ModelConvert_2.2 (located in the same directory as the RiverWare executable) can automatically perform the tasks.
Muskingum Routing on Reaches
Models using the muskingumRouting method on Reach objects must use the Input K and X Values method in the Routing Parameters method category. Users of the variable Muskingum Routing method should note that this method has been automatically changed to muskingumRouting. This is due to the creation of a new method category, Routing Parameters, which eliminates the need for the variable Muskingum Routing method.
Time Lag Reaches
TimeLagRouting on Reach objects now accommodates monthly lag times. This change requires the following:
1. If the timestep is monthly the lag time must be in months.
2. If the timestep is not monthly the lag time cannot be in months.
Variable Time Lag Routing
The variable TimeLagRouting method on Reach objects was modified to calculate Variable Lag Time using 3-D table interpolation. This requires only one table slot, the Variable LagTime Table (older models required four slots for this calculation: Date Range, Flow Range, Number of Seasons and Variable Lag Time Table). Models using this method need to add data to this new slot. The old slot used in this method, Variable Lag Time Table, no longer exists. This is conveyed by use of a warning message posted during model loading. More information about these changes can be found under the Reach heading below.
Seasonal GainLoss on Reaches
The Date Range slot on the Reach object has been changed to allow a range of days from 1 - 366 rather than the 0 - 365 range found in earlier versions of RiverWare. To obtain the same results, models using the Date Range table slot in the Seasonal GainLoss Flow Table method in the GainLoss Calculation category will need to add 1 to each value in the Date Range slot.
Pumped Storage Object
A new slot, Pumped Flow, was added to the Pumped Storage object. Models using this object must delete the link between the Reservoir object’s Flow TO Pumped Storage slot and the Pumped Storage object’s Inflow slot. This link must be replaced by a new link between Flow TO Pumped Storage and the new Pumped Flow slot. In addition, the Inflow slot (a required known) needs to be set to zero to achieve the same results.
Conjunctive Use on Water Users and AggDiversionSites
The Maximum (Total) Supplemental Request slots on Water User and lumped AggDiversionSite objects are now dependent on a method selected in the Maximum Supplemental Request category. If using these slots, the user must select the Input Maximum Request method in the Maximum Supplemental Request category (which is dependent on the Supplement Diversion method of the Conjunctive Use calculation category) to get the same model results.
Future Value Calculations
The calculateFutureValue method in the FutureValueCalcCategory on Reservoir and Pumped Storage objects has been altered to use a different set of slots. The Future Value of Water slot has been replaced by a slot called Marginal Storage Value Table. The calculation of Spill Cost and Future Value of Used Energy use this new slot. Models using the calculateFutureValue method must assign values to the Marginal Storage Value Table to avoid a table interpolation error.
Lumped Linking on AggDiversionSites
AggDiversionSites operating under the Lumped linking structure no longer set the Total Diversion Requested to 0.0 by default. All existing models that were using this default must now input zeros for the models to run correctly.
Model Loading
Some “SeriesSlots” changed to “AggSeriesSlots”
Some SeriesSlots have been converted to AggSeriesSlots. When loading old models, diagnostics messages may be generated as old slot types are automatically converted to new slot types:
Trying to convert former slot type (“SeriesSlot”) to new slot type (“AggSeriesSlot”).
Do not be concerned by these messages. You do not need to make any changes to your model. The use and functionality of these slots has not changed.
Simulation Objects
The following enhancements to the RiverWare simulation objects are described briefly. The user is encouraged to consult the Simulation Objects Documentation in the online help for more detailed descriptions of the enhancements to the objects and their methods.
Reach
Variable TimeLag Routing
The variableTimeLagRouting method has been modified to use a 3-D table interpolation to determine the Lag Time instead of a table lookup. This is accomplished through the use of a new tableslot, Variable LagTime Table. The Lag Time is computed based on a double interpolation involving the day of the year and the flow rate in the reach. Previous models using this method will no longer calculate Lag Time. New data is required in the Variable LagTime Table slot. Detailed documentation of this method may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Gain Loss
A new user method, Interpolated Flow GainLoss, was added to the Gain Loss Calculation category. This method (which is similar to the Seasonal GainLoss Flow Table method) uses values input according to the day of the year. Gain Loss is then determined by a three-dimensional table interpolation. Detailed documentation of this method may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Routing Parameters
A new method category, Routing Parameters, is available when muskingumRouting is selected in the routingMethodCategory. This new category contains methods for inputting muskingum coefficient data as either K and X values or C0, C1, and C2 coefficients (scalar or time series). The variableMuskingum routing method has been eliminated. Users of this method should select muskingumRouting and the Input Time Series K and X method in the Routing Parameters category to attain the same results. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
TimeLag Routing
Changes were made to timeLagRouting to conserve volume when using a monthly timestep and a monthly lag time. These changes require the user to use a monthly lag time if the timestep is monthly. Conversely, if the timestep is not monthly, a monthly lag time cannot be used.
Reach Bank Storage
A new method category, Reach Bank Storage Calculation, was added. Two methods are available: No Bank Storage and Average Flow Bank Storage. The Average Flow Bank Storage method is used to simulate hyporheic zone storage and return based on the flow rate in the reach. Detailed documentation of this method may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Seasonal GainLoss
The Date Range slot, used in the Seasonal GainLoss Flow Table method, is now one-based instead of zero-based. Users are required to increase the values in this slot by an integer of one to attain the same answers as in older models.
Interpolated GainLoss Uncertainty
A new method, Interpolated GainLoss Uncertainty, was added to the Reach Uncertainty Calculation category. This method enables users to perform uncertainty calculations based on the uncertainty of the gain/loss coefficients and is available only when the Interpolated Flow GainLoss method is selected in the GainLoss Calculation category. Detailed documentation of this method may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Water User
Input Diversion
Diversions may now be input on the Water User. This allows the object to solve given either Diversion or Diversion Requested. An additional dispatch method was added to accommodate these changes. The object may now dispatch with one of the following two methods: solveStandAlone_givenDivReqDepReq or solveStandAlone_givenDiversion.
There are some limitations to this design. If the user is using rules to set both Diversion and Diversion Requested at different priorities (for the same timestep), the object must always resolve using the same dispatch method. For example, suppose that Diversion Requested is set by a rule and the object dispatches given Diversion Requested. Then, a higher priority rule sets Diversion. The object should re-dispatch given Diversion. However, it will be forced to re-solve with the same dispatch method. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Return Flow Split Calculations
The returnFlowSplitCalculation methods now include the Supplement Return Flow as well as the Return Flow if Supplement Diversion is selected in the Conjunctive Use category. If Supplement Return Flow is being calculated, a new slot, Total Return Flow, is used to represent the sum of the Return Flow and Supplement Return Flow. It is the Total Return Flow that is split into surface and groundwater components. If Supplement Return Flow is not being calculated, the Total Return Flow slot is not visible and only the Return Flow is split. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Diversion and Depletion Request
Two new user methods, Population Requests and Regional Requests, were added to the Diversion and Depletion Request category. Population Requests is used to compute Diversion Requested and Depletion Requested based on the number of individuals in a population and the use rate per individual. Regional Requests is used to compute Diversion Requested and Depletion Requested based on the rate of water use for a region and the percentage of the region that applies to that particular rate. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Also, the name of the Agricultural Requests method was changed to Irrigation Requests.
Max Supplemental Request
A new method category, Max Supplemental Request, was added to enable the user to calculate values for the Maximum Supplement Request slot based on groundwater elevation. Three methods are contained within this Category: None, Input Maximum Request, and GW Elevation Maximum Request. The new method category is dependent on the Supplement Diversion method in the Conjunctive Use method category. Models previously using the Maximum Supplement Request slot must use the Input Maximum Request method to get the same results. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
AggDiversionSite
Input Diversion
Diversion may now be input on the AggDiversionSite. This allows the object to solve given either Total Diversion or Total Diversion Requested. An additional dispatch method was added for both the lumped and sequential linking structures to accommodate these changes. For the sequential structure, the object may now dispatch with one of the following two methods: processSequential_givenDivReq or processSequential_givenDiversion. For the lumped linking structure the two dispatch methods are: processLumped_givenDivReq and processLumped_givenDiversion. As a result of these modifications, an AggDiversionSite object operating under the lumped linking structure no longer sets the Total Diversion Requested to 0.0 by default. All existing models that were using this default must now input zeros for the models to run correctly.
There are some limitations to this design. If the user is using rules to set both Total Diversion and Total Diversion Requested at different priorities (for the same timestep), the object must always resolve using the same dispatch method. For example, suppose that Total Diversion Requested is set by a rule and the object dispatches given Diversion Requested. Then, a higher priority rule sets Total Diversion. The object should re-dispatch given Diversion. However, it will be forced to re-solve with the same dispatch method. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Total Diversion
The Sequential linking structure was modified so that Total Diversion is calculated as the lower value of Total Diversion Requested and Total Available Water. The Total Diversion is now propagated to the Incoming Available Water slot on the first WaterUser element. The Total Unused Water slot now represents the return flow from the Water User elements. Therefore old models must be updated in the following manner: 1.) Total Unused Water must be linked to the Return Flow slot on the object from which water is being diverted, 2) The link between Total Available Water and Incoming Available Water on the first WaterUser element must be deleted.
Maximum Supplemental Request
A new method category, Max Supplemental Request, was added to the AggDiversion Site for the lumped linking structure. This method category enables the user to calculate values for the Maximum Total Supplement Request slot based on groundwater elevation. Three methods are contained within this Category: None, Input Maximum Request, and GW Elevation Maximum Request. The new method category is dependent on the Supplement Diversion method in the Conjunctive Use method category. Models previously using the Maximum Supplement Request slot must use the Input Maximum Request method to get the same results. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Groundwater Storage
Storage Calculations
The storage calculations on the Groundwater Storage object were modified to prevent a negative Storage from being calculated. If the Outflow exceeds the flow rate required to drain the aquifer in a timestep, the Outflow is decreased to that flow rate. If calculating Percolation and the sum of the Outflow and Percolation exceeds the flow rate required to drain the aquifer in a timestep, then both Outflow and Percolation are proportionally decreased so the sum of the two is equal to that flow rate. If however, Percolation is input, only Outflow is decreased. Detailed documentation of these calculations is available in the Dispatch Methods section of the Simulation Objects Documentation .
Previous Elevation Calc
A new method category, Previous Elevation Calc, enables the user to input or calculate the previous timestep’s water table elevation based on the previous storage. The Previous Groundwater Elevation slot is used in conjunction with the Water User to determine the Maximum Supplement Request. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Confluence
Pre-simulation Dispatching
The Confluence object may now dispatch before the start of the run. The object checks upstream to obtain the earliest timestep at which an upstream object dispatches. Provided that its dispatch conditions are met, the Confluence may then dispatch at the earliest dispatch timestep of any upstream object.
Old models may be adversely affected by this change. If the Confluence object contains data before the start of the run, it may now solve and propagate data to other objects. Likewise, if the Confluence receives data from an upstream object it may now try to solve in an overdetermined state. In either case, the result is an overdetermination error expressed by one of the following error messages:
“Object is overdetermined”
“Attempting to set slot from multiple sources”
These errors may or may not be generated from the Confluence itself. The problem is fixed by deleting the excess data on the Confluence object for all pre-simulation timesteps.
Diversion Object
Diversion Request Calculation
A new method category, Diversion Request Calculation, is available on the Diversion Object. The default method, Input Diversion Request, performs no calculations. The Percent of Available method computes Diversion Requested as a specified percentage of the available water. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Reservoir Objects
Dispatch Method Change
The solveMB_givenInflowReleaseRegSpill dispatch method was changed to solveMB_givenInflowRelease. The Regulated Spill slot is no longer a required known for the object to dispatch with this method. Also, the dispatch method is available regardless of the spill method in use. Detailed documentation of these methods may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Power Coefficient
The Best Power Coefficient and Max Power Coefficient tables are now used whenever the BEST or MAX flag is set on Energy (regardless of whether or not the Power Coefficient is input).
Pumped Storage Object
Upstream Inflows
The Pumped Storage Object is now able to model inflows from upstream. This enhancement required a change in slot notation. The flow into the reservoir as a result of pumping is accounted/calculated for in the Pumped Flow slot. The Inflow slot is used to represent inflow into the reservoir from upstream. Currently the object is only allowed to solve downstream (i.e. Inflow must be input and cannot be calculated). Old models using this object require three changes: the link between Inflow and Flow TO Pumped Storage must be removed, a link must be created between Pumped Flow and Flow TO Pumped Storage, and Inflow must be set to zero. Detailed documentation of this object may be found in the Simulation Objects Documentation online.
Rulebased Simulation
Documentation is now available for the pre-defined functions used in Rulebased Simulation. The documentation is reached by selecting Browse Rulebased Simulation Documentation from the online help menu.
Closing a Ruleset
A loaded ruleset is no longer allowed to be closed while remaining loaded. If a loaded ruleset is closed, the ruleset is automatically unloaded. The user will be asked to confirm this action upon closing the ruleset.
Print Statements
PRINT statements now always execute when their containing rule executes, regardless of whether or not any other statements within that rule succeed or not. Also, PRINT statements failing will not cause the containing rule to fail. E.g., if a PRINT statement encounters a NaN, a diagnostic is issued noting this fact, but the rule containing that print statement continues execution (as if nothing had happened).
When a RuleExpr is printed out by a PRINT statement or by a diagnostic, the RuleExpr’s text should be more readable, but could be different from what the user would see if they looked in a model file containing the same expression.
Units
All NumericValues now have units. If none are specified then units of NONE are added. Textual representations of NumericValues with units of NONE do not have any unit string.
For the user this means they no longer need to type in units if there aren’t any. Units will now default to NONE, and units of NONE will never show up. This means that users now need to be a bit more careful about units because we aren’t as likely to notice when they forget and leave off units.
Name Checking
Checking was added to prevent the same name from being used multiple times in the same namespace. This was done to prevent the user from accidentally “hiding” a variable in an outer scope by declaring a variable of the same name in an inner scope.
An example of what is not allowed:
WITH (x = 1.0) DO
WITH (x = 2.0) DO
x
ENDWITH
ENDWITH
Did the writer really intend to refer to the innermost x? Maybe not. This problem can be corrected by changing either variable name:
WITH (x = 1.0) DO
WITH (y = 2.0) DO
x
ENDWITH
ENDWITH
This problem will be detected and reported by RiverWare whenever a ruleset is validated (to the CONSISTENT level), i.e., when the user explicitly asks to validate a rule or when the ruleset is executed.
Note that this change actually applies to all named objects, meaning variables as well as functions. If a function is accessible (may be called) from an expression, then its name may not be used as the name of a variable.
Division By Zero
There is now a check for division by zero; both normal division and integer division (==- “/” and “DIV”). If the divisor is zero, then an error is issued (at evaluation time) and the rule fails.
Rule Language Functions
IsNaN
IsNaN is now a built-in function of the Rule Language and not a predefined function (i.e. it is now represented by a button on the palette). It returns true if a NaN is encountered anywhere in the evaluation of the operand expression, false otherwise. Before it only returned true if the operand was a simple expression involving only an object/slot lookup. If it was more complicated and a NaN was encountered, then the execution failed (reporting that a NaN was encountered).
REMOVE
Returns a list which is identical to the given list except the item at the given position has been removed (positions begin with index 0).
SUB
Returns a list which is identical to the given list except the item at the given position has been replaced with the specified expression.
WITH = DO, ENDWITH
This defines variable, binds it to the value resulting from the evaluation of the “variable expression”, then returns the result of evaluating the “body expression” within the scope of this value.
Predefined Functions
Two predefined functions have been added to the Rulebased Simulation Palette. The new functions, as well as all of the existing functions, are described in the Simulation Objects Documentation online. Following is a list of new predefined functions:
DATETIME OffsetDate (DATETIME, NUMERIC, STRING)
where the string specifies a timestep (as with the predefined function GetDates()), which is added to the DATETIME argument an integral number of times given by the NUMERIC argument (rounded down, units must be “NONE”). The resulting DATETIME is returned.
OBJECT GetObject (STRING objectName)
Given the name of an object, finds and returns the object of with that name.
Net Subbasin Diversion Requirement
The pre-defined function NetSubbasinDiversionRequirement now uses the MinBypass slot on the reach (if it exists and is known) as the minimum flow. Detailed documentation of this method may be found in the Rulebased Simulation Documentation online.
Diversion Object with Rules
The NetSubbasinDiversionRequirement and NonShortDiversionRequirement functions now work with the Diversion Object as well as AggDiversionSites.
GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Menu Bar
Import Object(s) and Export Object(s) menu items were added to the Model menu in the main workspace menubar. A new submenu was added to the Workspace menu. WorkspaceObjects contains all options that apply to objects on the workspace.
Open Object Dialog
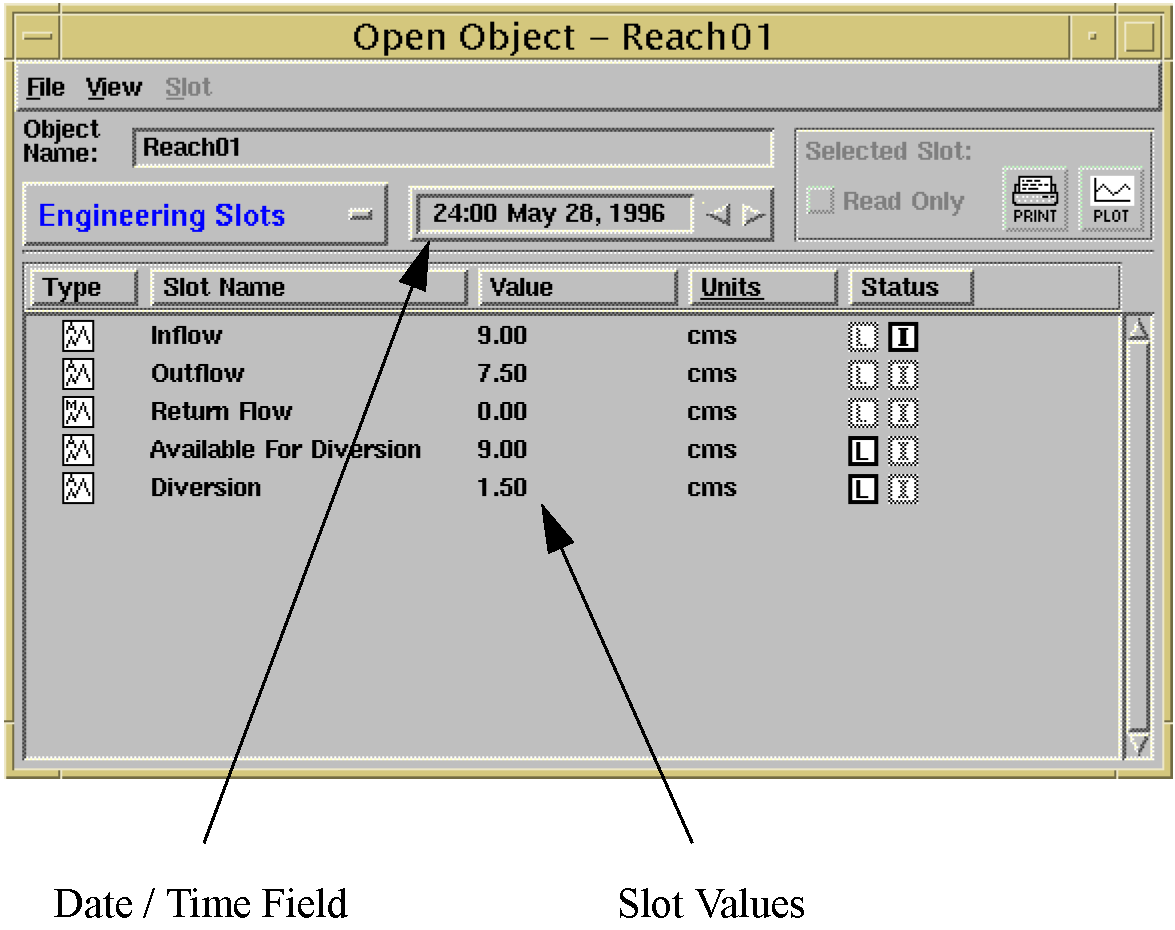
The appearance of the Open Object dialog has changed slightly. The most notable difference is the addition of a date/time field. The numbers shown in the Value field (to the right of the Slot Name field) are the slot values for the timestep expressed in the date/time field above. The left and right arrows in the date/time field can be used to move the date forwards or backwards. The number shown in the Value field will change accordingly. The figure on the following page shows the new appearance of the Open Object dialog.
Closed Bug Reports
The following is a list of the bugs which were fixed for this release. If you wish to view the details for a specific bug, please browse to http://cadswes.colorado.edu/users/gnats-query.html and search our bug database. You will need a RiverWare user login and password.
829 | 845 | 901 | 916 | 940 | 1035 | 1113 |
1273 | 1339 | 1376 | 1452 | 1453 | 1466 | 1471 |
1480 | 1483 | 1510 | 1531 | 1535 | 1540 | 1542 |
1568 | 1570 | 1617 | 1646 | 1668 | 1672 | 1696 |
1706 | 1724 | 1732 | 1751 | 1754 | 1760 | 1768 |
1795 | 1812 | 1815 | 1816 | 1819 | 1828 | 1830 |
1838 | 1851 | 1857 | 1861 | 1862 | 1866 | 1867 |
1869 | 1870 | 1901 | 1906 | 1911 | 1912 | 1924 |
1925 | 1932 | 1945 | 1978 | 1990 | 1993 | 2008 |
2037 | 2048 | 2049 | 2050 | 2055 | 2056 | 2057 |
2058 | 2064 | 2066 | 2067 | 2068 | 2069 | 2077 |
2084 | 2088 | 2093 | 2097 | 2100 | 2102 | 2111 |
2114 | 2120 | 2127 | 2128 | 2137 | 2138 | 2139 |
2140 | 2147 | 2148 | 2149 | 2150 | 2151 | 2153 |
2154 | 2155 | 2156 | 2158 | 2159 | 2160 | 2163 |
2164 | 2167 | 2171 | 2172 | 2173 | 2175 | 2177 |
2178 | 2180 | 2181 | 2182 | 2184 | 2186 | 2187 |
2189 | 2193 | 2196 | 2202 | 2203 | 2204 | 2205 |
2206 | 2207 | 2208 | 2209 | 2213 | 2214 | 2215 |
2218 | 2219 | 2223 | 2226 | 2227 | 2228 | 2231 |
2233 | 2234 | 2235 | 2236 | 2237 | 2239 | 2241 |
2243 | 2246 | 2253 | 2254 | 2256 | 2257 | 2266 |
2267 | 2268 | 2271 | 2272 | 2275 | 2282 | 2283 |
2285 | 2286 | 2287 | 2289 | 2292 | 2293 | 2294 |
2295 | 2296 | 2297 | 2299 | 2303 | 2304 | 2306 |
2307 | 2309 | 2310 | 2311 | 2312 | 2313 | 2314 |
2315 | 2316 | 2317 | 2323 | 2325 | 2327 | 2328 |
2329 | 2330 | 2333 | 2334 | 2336 | 2340 | 2342 |
2343 | 2344 | 2358 | 2360 | 2362 | 2375 | 2379 |
2384 | 2385 | 2386 | 2387 | 2388 | 2389 | 2391 |
2394 | 2396 | 2404 | 2406 | 2407 | 2410 | 2412 |
2417 | 2423 | 2429 | 2431 | 2435 |
Revised: 11/11/2019